Deployment Considerations
The components and operations required to deploy an ICE Server depend on the host environment, the network topology, the source of the installation files, and security. You must determine these options before you deploy.
The following image illustrates the available installation options.
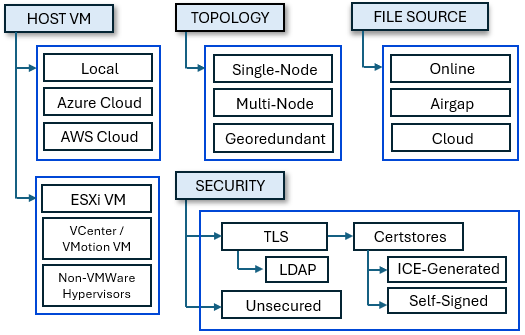

In the diagram above, the decisions are shown in blue and connected by arrows to the selectable options
A simple Local deployment would involve installing a Single-Node ICE Server on an ESXi VM using Airgap or Online files. (Airgap is recommended for installations with slow internet connections).
Deploying an ICE Server to a cloud-based server environment requires a subscription to a supported cloud provider for hosting and storage of the ICE Server and satellite components. Instant Connect does not provide cloud-hosting resources.
Bare metal deployments are also possible. Contact Instant Connect Support for technical details.
HOST VM
All hosts, local or cloud, require a supported VM. Determine the locality of your deployment and then determine the VM that will host the ICE Server OS. Bare metal deployments are also possible.
TOPOLOGY
The term ‘Node,’ in this context, indicates an instance of ICE Server.
A single-node deployment consists of one ICE Server only. It has no failover.
Multi-node deployments involve 3 or more ICE Servers operating in failover mode. This allows expandible redundancy where additional nodes can be added if needed.
Georedundant deployments involve 2 ICE Servers configured specifically for failover. The redundant server (DC2) maintains a running data connection with the active ICE Server (DC1). If the active server goes down, the georedundant server activates and takes over where it left off with minimal interruption.
Georedundant instructions are called out in procedures when specific configurations are required.
FILE SOURCE
Where the installation files reside determines how they can be installed. You can download the ICE Enterprise or Air Gap installers from the ICE Support Portal. You can also install the ICE Server from a cloud repository to a local or cloud server.
Air Gap instructions are called out in procedures when specific configurations are required.
For host machines with good internet connections, you can download the ICE Server Installation .zip Be aware that an internet connection is required to download components required for your configuration. Airgap is recommended if your connection is too slow or prone to disconnection.
Designed for security and offline deployments, the ICE Airgap deployment files contain all necessary packages to run an ICE Server and any required satellite components in a supported environment. No other downloads are required, allowing for portability and offline ICE deployments.
Instant Connect support cloud installations via Amazon ECR pull-through caching using the ICE OS Configuration Wizard and Docker Hub.
SECURITY
The ICE OS Installation Wizard can create certificates and certstores for you, or you can upload your own certificates. You also have the option of deploying without TLS.